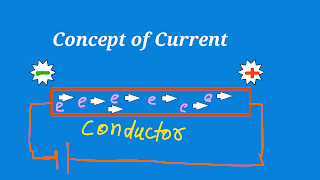
Current (I) : Current can be defined as rate of flowing of charge (Q).
i.e
I= Q/t
where Q= Charge in coulumb
I = current in Ampere
t= Time in second.
1 Ampere is the charge flowing through a conductor in 1 second.
Q= I x T Amp-Sec
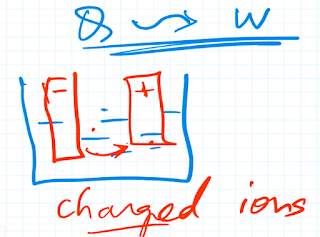
In an ionized electrolyte charged ions flow from one plate to another. For example, negative ions flow from the cathode to the anode and positive ions flow from the anode to the cathode.
charge of 1 e = 1.6×10-19 Coulomb
or 6.25×1018 electrons= 1 coulomb